What is a Security & Compliance Center in O365?
- Manages compliance across Office 365, Exchange Online, and SharePoint Online.
- Manages archive mailboxes, eDiscovery cases, auditing reports, and retention and deletion policies in Exchange Online and SharePoint Online.
- Assigns permissions to compliance managers for access to some or all of the compliance features in the Security & Compliance Center.
This document is an overview of Office 356 Security and Compliance Center.
Physical Security
- Customer data stored in Office 365 datacenters are geographically distributed and their locations are not disclosed as a standard policy.
- Datacenters are built to withstand natural disasters. Access is provided to essential personnel only. Access is monitored 24 hours day by job function subject to customer application and services.

- Physical access control is segregated into multiple authentication and security processes, including badges and smart cards, biometric scanners, on-premises Security officers, continuous video surveillance, and two-factor authentication with motion sensors, video surveillance, and security breach alarms.
- The internal datacenter network is segregated from the external network. Networks within the Office 365 datacenters are further segmented to provide physical separation of critical back-end servers and storage devices from the public-facing interfaces.
- Faulty drives and hardware are demagnetized and destroyed.
Data Security
- Encryption at rest protects data while on the servers.
- Encryption in transit with SSL/TLS protects data when it’s transmitted between you and Microsoft.
- Threat management, security monitoring, and file/data integrity prevent or detect any tampering of data.
- Exchange Online Protection provides advanced security and reliability against spam and malware to help protect your information and access to email.
- No Mining or Accessing of Data for Advertising Purposes is allowed.
- Data is not lost or destroyed when a customer’s Subscription is terminated.
- Encrypted email ensures no one other than the intended recipient can open and read emails.
- Advanced Threat Protection includes protection for SharePoint Online, Word, Excel, PowerPoint and OneDrive for Business.
- Regular backups of data are taken to avoid data loss. Alerts are sent to users if data has been accessed improperly.
Import Service
- Office 365 Import Service imports PST files to Exchange Online mailboxes or to import data files to the SharePoint Online organization.
- For both types of files, they may be uploaded over the network or copied to a hard drive and then shipped to a Microsoft datacenter, for import into Office 365.
Prevent Breach
Microsoft continues to improve its built-in security features including port scanning, perimeter vulnerability scanning, system patches, network level isolation/breach boundaries, DDoS detection and prevention, and multi-factor authentication for service access to prevent breaches.
Detect Breach
Microsoft uses a form of machine learning, utilizing signals from their internal system security alerts and combining them with external signals such as customer incidents, to detect patterns and trigger alerts.
Respond to Breach
In the event of a security compromise, Microsoft launches its incident response process, which includes immediate termination of access to sensitive data while informing the affected parties.
Recover from Breach
This step returns the cloud service to operation, automatically updating and auditing breached systems to detect anomalies.
Logical Security
- Lockbox processes for a strictly supervised escalation process greatly limit human access to data.
- Servers run only processes that are whitelisted, minimizing the risk from malicious code execution.
- Dedicated threat management teams proactively anticipate, prevent, and mitigate malicious access.
- Port scanning, perimeter vulnerability scanning, and intrusion detection prevent or detect any malicious access.
- Microsoft employs anti-malware software to protect data from malicious applications by both detecting and preventing such software from entering the systems.
- If malware enters a system, Microsoft quarantines infected systems to prevent additional damage. Additionally, they perform regular updates, hotfixes, and patches.
Anti-spam and anti-malware protection
- Office 365 has built-in malware and spam filtering capabilities that help protect inbound and outbound email messages from malicious software and to help protect from spam.
- The filtering technologies are enabled by default. Additionally, they may be customized with company-specific filtering policies.
- Examples of O365 Spam, Malware & Connection Filter Options which includes
- Detection response for spam : Quarantine /Move to Junk Folder
- Detection response for high confidence spam : Quarantine /Move to Junk Folder
- Mark bulk email as spam : Enabled
- Threshold : 9 ( Highest level for Spam filter)
- Sender block list : Configured with 835 entries
- Domain block list : Configured with 590 entries
- Sender allow list : Configured with 879 entries
- Domain allow list : Configured with 15070 entries
- International spam – languages : Enabled 22
- International spam – regions : Enabled 10
- Blocked IP : Configured with 114 entries
- File types blocked : .ace .ani .app .docm .exe .jar .reg .scr .vbe .vbs
User Control
- Office 365 Message Encryption allows users to send encrypted email to anyone, regardless of what email service recipients may use.
- Data loss prevention can be combined with Rights Management and Office 365 Message Encryption to give greater controls to each organization’s admins to apply appropriate policies to protect sensitive data.
- S/MIME provides message security with certificate-based email access.
- Azure Active Directory is used as the underlying identity platform which enables each tenant with strong authentication and Azure Rights Management to prevent file-level access without the proper user credentials.
- Client-based access controls, allow organizations to specify how users access information from specific devices or specific locations or a combination of both (for example, limiting access from public computers or from public open Wi-Fi)
- Role-based access control (RBAC) are also present. They are similar to the access control procedures for Microsoft datacenters described earlier in the “Automated operations” section.
- Multi-factor authentication enhances user level security where users will be prompted for OTP or CALL to login to Office365 portal.

Archiving
- Archiving manages the information lifecycle in Office 365 by automatically archiving older and infrequently accessed content, and by removing older content that is no longer required.
- It includes archive mailboxes, retention policies, overview of document deletion policies and records management.
Admin Control
- Administrators have full control and can customize the level of restrictions for users in their organization. For example, users can simply be warned about sensitive data before sending it, sending sensitive data can require authorization, or users can be blocked from sending data completely.
- DLP (data loss prevention) features scan both email messages and attachments, and administrators have access to comprehensive reporting about what data is being sent by whom.
- Multi-factor authentication protects access to the service with a second factor such as phone.
- Data loss prevention prevents sensitive data from leaking either inside or outside the organization while providing user education and empowerment.
- Built-in mobile device management capabilities control access to corporate data by mobile devices.
- Mobile application management within Office mobile apps powered by Intune provides granular controls to secure data contained in these apps.
- Built in antivirus and antispam protection along with advanced threat protection safeguard against external threats.
- Office 365 Cloud App Security provides enhanced visibility and control into each Office 365 environment.
Data loss prevention
- Data loss prevention (DLP) helps to protect sensitive information and prevent its inadvertent disclosure.
- Examples of sensitive information that you might want to prevent from leaking outside your organization include financial data or personally identifiable information (PII) such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, or health records.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) policies identify, monitor, and automatically protect sensitive information across Office 365.
eDiscovery
- Electronic discovery, or eDiscovery, is the process of identifying and delivering electronic information that can be used as evidence in legal cases.
- Using eDiscovery in Office 365 to search for content in Exchange Online mailboxes, SharePoint Online sites, or both.
- It is used to identify, hold, and export content found in Exchange mailboxes and SharePoint sites.
Hold
- Hold allows you to preserve or archive content for compliance and eDiscovery.
- The types of hold include an overview of preservation policies in the Office 365 Security & Compliance Center as well as In-Place Hold and Litigation Hold in Exchange Online.
Inactive mailboxes
- An inactive mailbox is used to preserve a former employee's email after he or she leaves your organization.
- A mailbox becomes inactive when a Litigation Hold or an In-Place Hold is placed on the mailbox before the corresponding Office 365 user account is deleted.
- The contents of an inactive mailbox are preserved for the duration of the hold that was placed on the mailbox before it was made inactive.
- Administrators, compliance officers, or records managers can use eDiscovery in Office 365 to access and search the contents of an inactive mailbox.
Mobile Device Management
- You can use Office 365 to secure and manage any device that uses Exchange ActiveSync to sync with your organization’s email, calendar, contacts, and tasks.
- Using the Office 365 and Exchange admin centers, you can perform common mobile device management tasks like setting device access rules, viewing device reports, and remotely wiping devices that are lost or stolen.
Transport Rules
- Using transport rules, you can look for specific conditions in messages that pass through your organization and take action on them.
- Transport rules let you apply your business policies to email messages and they can help secure messages, protect messaging systems, and prevent information loss.
- You can use the Exchange Admin Center or Windows PowerShell to manage transport rules.
Auditing & Retention Policies
- Users can log events, including viewing, editing, and deleting content such as email messages, documents, task lists, issues lists, discussion groups, and calendars.
- When auditing is enabled as part of an information management policy, administrators can view the audit data and summarize current usage.
- Administrators can use these reports to determine how information is being used within the organization, manage compliance, and investigate areas of concern.
- For business, legal, or regulatory reasons, you may have to retain e-mail messages sent to and from users in your organization, or you may want to remove e-mail that you aren't required to retain.

- Messaging records management (MRM), the records management technology in Office 365, enables you to control how long to keep items in users' mailboxes and define what action to take on items that have reached a certain age.
- Assigning retention policy tags to default folders, such as the Inbox and Deleted Items.
- Applying default policy tags to mailboxes to manage the retention of all Untagged items.
- Allowing the user to assign personal tags to custom folders and individual items.
Auditing
- You can use the auditing functionality in Office 365 to track changes made to your Exchange Online configuration by Microsoft and by your organization’s administrators and changes made by users to documents and other items in the site collections of your SharePoint Online organization.
- After you turn on auditing to capture admin and user actions, you can view audit reports and export the audit logs.
Information management policies
- An information management policy is a set of rules for a type of content. In SharePoint Online, information management policies enable organizations to control and track things such as how long content is retained or what actions users can take with that content. Predefined policies include retention policies, expiring out-of-date content, and auditing of document usage.
- You can use site policies to help control site proliferation. A site policy defines the lifecycle of a site by specifying when the site will be closed and when it will be deleted.
Information Rights Management
Information Rights Management (IRM) helps prevent sensitive information from being printed, forwarded, saved, edited, or copied by unauthorized people.
Advanced Threat Management
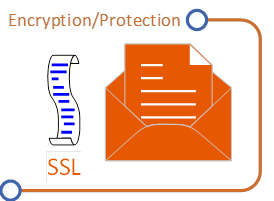
- Reports are used to obtain better insights as to malware activity
- Get deeper protection against malicious URL’s with filtering features:
- Sender Policy Framework
- Conditional Sender ID filtering: hard fail:
- NDR backscatter
- Apply sensitive word list
- Empty messages
- Numeric IP address in URL
- URL redirect to other port
- URL to .biz or .info websites
- JavaScript or VBScript in HTML
- Frame or IFrame tags in HTML
- Object tags in HTML
- Embed tags in HTML
- Web bugs in HTML

- O365 involves continuous improvements to service-level security features
- Port scanning and remediation
- Perimeter vulnerability scanning
- Operating system security patching
- Network-level distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) detection and prevention
- Multi-factor authentication for service access
- Auditing all operator/administrator access and actions
Quarantine
- Email messages are quarantined when they are classified as malware, spam, phish, or bulk email or because of a transport rule setting in your organization.
- Review the messages and decide whether you want to release them to one or more of the intended recipients.

Quarantine Options are available for Administrators to choose what their organization needs
- Release selected message & allow sender – message will be released to all recipients it's addressed to and all future messages from this sender will be allowed but not the sender domain. Example it will release only emails from user@advansit.com and not from advansit.com
- Release message to specific recipients – this will release messages to specific recipients without reporting it as a false positive within a group of recipients. Like email sent to User1, User2, User3, User4 & by selecting this option we are forcing this message to get released only for User2 & User3 and not for rest of them and we are avoiding to report it as false positive to Microsoft.
- Release message to All recipients – this will release messages to all recipients like User1, User2, User3, User4 etc... And not only to specific person by not sending false positive to Microsoft.
- Release selected messages & report as false positive - will release the message to your inbox and report it not as spam to the Microsoft Spam Analysis Team, who will evaluate and analyze the message and Depending on the results of the Microsoft analysis, the service-wide spam content filter rules may be adjusted to allow the message through.
Top 10 Compliance Areas of Office 365
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA imposes on customers that may be “covered entities" under the law security, privacy, and reporting requirements regarding the processing of electronic protected health information. Microsoft developed Office 365 to provide physical, administrative, and technical safeguards to help our customers comply with HIPAA. Microsoft offer a HIPAA Business Associate Agreement (BAA) to any customer.
- Data processing terms: Microsoft provides customers with additional contractual assurances through its data processing terms regarding handling and safeguarding of customer data. By agreeing to these terms, Microsoft implements over 40 specific security commitments collected from regulations worldwide. The robust commitments in data processing terms are available to customers by default.
- Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA): requires U.S. federal agencies to develop, document, and implement controls to secure their information and information systems. Federal Risk and Authorization Program (FedRAMP) is a federal risk management program that provides a standardized approach for assessing and monitoring the security of cloud products and services.
- ISO 27001: ISO 27001 is one of the best security benchmarks available in the world. Many products in Office 365 have been verified to meet the rigorous set of physical, logical, process and management controls defined by ISO 27001:2013. This also includes ISO 27018 Privacy controls in the most recent audit. Inclusion of these new ISO 27018 controls in the ISO assessment will further help Office 365 validate to customers the level of protection Office 365 provides to protect the privacy of customer data.
- European Union (EU) Model Clauses: The EU Data Protection Directive, a key instrument of EU privacy and human rights law, requires customers in the EU to legitimize the transfer of personal data outside of the EU. The EU model clauses are recognized as a preferred method for legitimizing the transfer of personal data outside the EU for cloud computing environments. Offering the EU model clauses involves investing and building the operational controls and processes required to meet the exacting requirements of the EU model clauses. Unless a cloud service provider is willing to agree to the EU model clauses, a customer might lack confidence that it can comply with the EU Data Protection Directive's requirements for the transfer of personal data from the EU to jurisdictions that do not provide “adequate protection" for personal data.
- ISO 27018: Microsoft is the first major cloud service provider to be independently verified as complying with ISO 27018, which establishes a uniform, international approach to protecting the privacy of personal information stored in the cloud. Office 365 compliance with ISO 27018 means that O365 only process personal information in accordance with customer instructions, we are transparent about what happens to customer data, we provide strong security protections for personal information in our cloud, customer data will not be used for advertising, and Microsoft inform customers about government access to their data.
- Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA): FERPA imposes requirements on U.S. educational organizations regarding the use or disclosure of student education records, including email and attachments. Microsoft agrees to use and disclosure restrictions imposed by FERPA that limit our use of student education records, including agreeing to not scan emails or documents for advertising purposes.
- Statement on Standards for Attestation Engagements No. 16 (SSAE 16): Office 365 has been audited by independent third parties and can provide SSAE16 SOC 1 Type I and Type II and SOC 2 Type II reports on how the service implements controls.
- Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act (GLBA): The Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act requires financial institutions to put processes in place to protect their clients' nonpublic personal information. GLBA enforces policies to protect information from foreseeable threats in security and data integrity. Customers subject to GLBA can use Office 365 and comply with GLBA requirements.
- Health Information Trust Alliance (HITRUST): The Office 365 team, in partnership with an independent assessor, has completed an assessment to evaluate compliance with HITRUST. Viewed as an important standard by U.S. healthcare organizations, HITRUST has established the Common Security Framework (CSF), a certifiable framework that can be used by any and all organizations that create, access, store or exchange personal health and financial information.
Source from Microsoft